The electric vehicle (EV) industry has entered a defining phase in 2026. While vehicle design, charging infrastructure, and software continue to evolve, the battery remains the most critical and cost-defining component of any electric vehicle. Battery pricing directly influences EV affordability, manufacturer margins, government incentives, and long-term adoption rates.
Why EV Battery Cost Matters More Than Ever in 2026
In 2026, global EV sales continue to rise, but battery cost remains the primary barrier to mass affordability. Even as production scales, batteries still account for 30% to 45% of total EV manufacturing cost, depending on vehicle type and chemistry.
Battery pricing affects:
-
Vehicle retail prices
-
Profit margins for automakers
-
Leasing and financing models
-
Total cost of ownership (TCO)
-
Government subsidy dependency
As subsidies gradually phase out in many regions, battery cost reductions are now essential for sustainable EV growth.
Average Electric Vehicle Battery Cost in 2026
Battery costs are commonly measured in cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh). In 2026, the global average continues to decline but at a slower pace compared to earlier years.
Global Average EV Battery Cost (2026)
| Battery Type | Average Cost per kWh (USD) | Typical Vehicle Segment |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Iron-Phosphate (LFP) | $75 – $95 | Entry-level & fleet EVs |
| Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) | $100 – $125 | Mid-range passenger EVs |
| Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum (NCA) | $110 – $135 | Premium & long-range EVs |
| Sodium-Ion | $60 – $80 | Urban & budget EVs |
These prices reflect cell-level costs, excluding battery pack integration, thermal management, and vehicle-specific engineering.
Total Battery Pack Cost by Vehicle Type
The final cost consumers indirectly pay is the battery pack cost, not just individual cells.
Estimated Battery Pack Cost in 2026
| Vehicle Category | Battery Size (kWh) | Estimated Battery Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Small city EV | 30 – 40 kWh | $3,000 – $4,500 |
| Compact sedan | 50 – 60 kWh | $5,000 – $7,000 |
| SUV | 70 – 90 kWh | $7,500 – $11,000 |
| Long-range premium EV | 100+ kWh | $12,000 – $15,000 |
Battery pack costs still define price differences between EV trims and range variants.
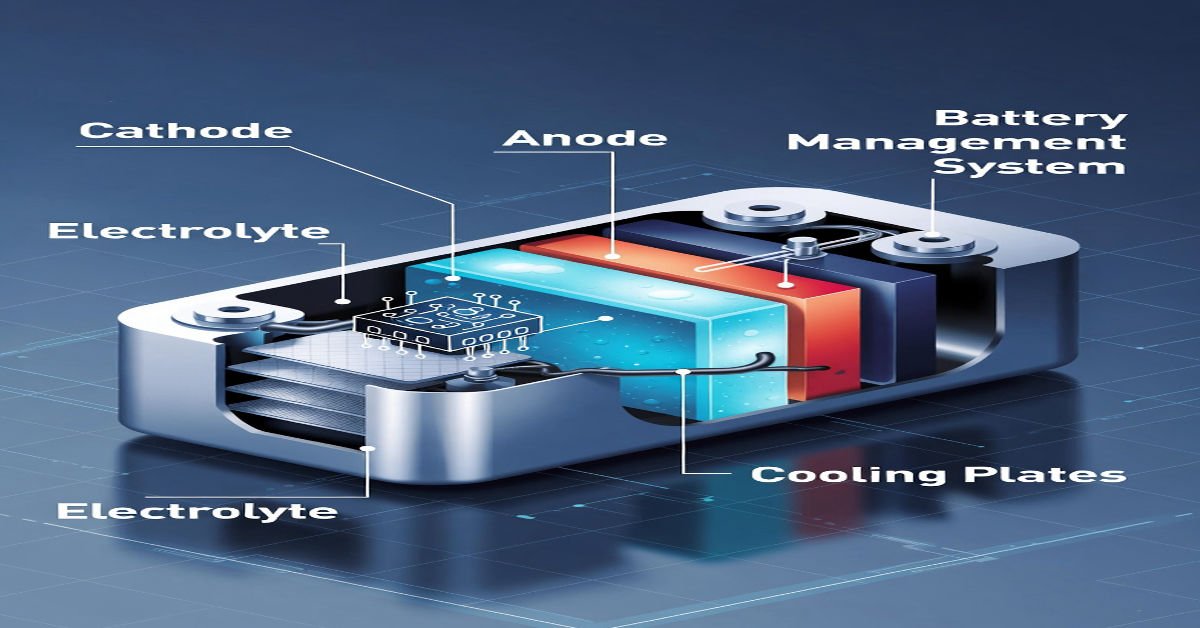
Key Components Driving EV Battery Costs
Understanding battery pricing requires breaking down its internal cost structure.
EV Battery Cost Breakdown (2026)
| Component | Share of Total Cost |
|---|---|
| Cathode materials | 35% – 40% |
| Anode materials | 10% – 15% |
| Electrolyte & separator | 10% |
| Manufacturing & assembly | 20% – 25% |
| Battery management system (BMS) | 5% – 8% |
| Thermal management & casing | 5% – 7% |
Among these, cathode materials remain the most expensive, especially those containing nickel and cobalt.
Impact of Raw Material Prices in 2026
Raw material markets heavily influence battery economics. While lithium prices stabilized compared to earlier volatility, nickel and graphite costs remain sensitive to global supply chains.
Major Raw Materials and Cost Influence
| Material | Role in Battery | 2026 Cost Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium | Energy storage | Stable |
| Nickel | Energy density | Moderately rising |
| Cobalt | Thermal stability | Gradually declining |
| Graphite | Anode material | Region-dependent |
| Manganese | Cost reduction | Stable |
Manufacturers are actively reducing cobalt dependency to improve cost predictability and ethical sourcing.
Battery Chemistry Trends Shaping Costs
Battery chemistry choices significantly impact pricing strategies in 2026.
Lithium-Iron-Phosphate (LFP)
LFP batteries dominate cost-focused segments due to:
-
No cobalt or nickel
-
Longer cycle life
-
Lower fire risk
-
Lower production cost
They are now widely used in mass-market EVs, taxis, and delivery fleets.
Nickel-Based Batteries (NMC & NCA)
Nickel-rich chemistries remain preferred for:
-
High energy density
-
Longer driving range
-
Performance vehicles
However, their higher material cost keeps them reserved for mid-to-premium models.
Sodium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-ion technology gained traction in 2026 as:
-
A low-cost alternative
-
Suitable for short-range urban EVs
-
Less dependent on scarce materials
While energy density is lower, cost advantages are compelling for emerging markets.
Regional EV Battery Cost Comparison
Battery manufacturing location plays a critical role in pricing.
EV Battery Cost by Region (2026)
| Region | Avg Cost per kWh | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| China | $70 – $95 | Scale, local supply chains |
| Europe | $110 – $135 | Higher labor & energy costs |
| North America | $105 – $130 | Domestic manufacturing push |
| India | $90 – $110 | Growing localization |
| Southeast Asia | $85 – $105 | Emerging gigafactories |
China continues to lead in cost efficiency due to vertical integration and massive production volumes.
Manufacturing Scale and Gigafactories
The expansion of gigafactories worldwide has reduced costs through:
-
Automation
-
Higher yields
-
Lower defect rates
-
Localized supply chains
By 2026, most major automakers either own or partner in battery production, reducing reliance on external suppliers and improving pricing control.
Battery Cost vs EV Price: Consumer Impact
Despite declining battery prices, EV sticker prices do not always fall proportionally. This is due to:
-
Inflation in other vehicle components
-
Software and ADAS features
-
Compliance with safety regulations
-
Marketing and distribution costs
However, battery cost reductions still improve long-term affordability through lower financing and leasing rates.
Battery Degradation and Lifetime Value
Cost analysis must include battery lifespan.
Average Battery Lifespan in 2026
| Battery Type | Expected Cycles | Estimated Vehicle Life |
|---|---|---|
| LFP | 3,000 – 5,000 | 12 – 15 years |
| NMC | 1,500 – 2,500 | 8 – 12 years |
| NCA | 1,200 – 2,000 | 8 – 10 years |
Longer lifespan reduces cost per mile, making some lower-density batteries more economical over time.
Second-Life and Recycling Economics
Battery cost analysis in 2026 increasingly includes residual value.
Used EV batteries are repurposed for:
-
Grid storage
-
Solar energy systems
-
Backup power
Recycling technologies now recover:
-
Lithium
-
Nickel
-
Cobalt
-
Copper
This recovery reduces future raw material costs and improves sustainability metrics.
Government Policies and Cost Influence
While direct subsidies are declining, governments still support cost reduction through:
-
Local manufacturing incentives
-
Recycling mandates
-
Import duty exemptions
-
Research funding
Such policies indirectly lower battery costs by stabilizing supply chains and encouraging innovation.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Perspective
When analyzing battery cost, total ownership cost matters more than upfront price.
EVs benefit from:
-
Lower maintenance
-
Reduced fuel costs
-
Longer drivetrain lifespan
Even in 2026, EVs with higher initial battery costs often deliver lower lifetime expenses compared to internal combustion vehicles.
Future Battery Cost Forecast Beyond 2026
Industry analysts expect:
-
Gradual cost reductions rather than sharp declines
-
Increased use of alternative chemistries
-
Greater standardization across platforms
Projected Battery Cost Trend
| Year | Estimated Avg Cost per kWh |
|---|---|
| 2026 | $85 – $120 |
| 2028 | $70 – $100 |
| 2030 | $60 – $90 |
Innovation now focuses on supply stability and sustainability, not just raw cost reduction.
Expert Insights and Industry Consensus
Battery engineers and industry leaders agree that:
-
Material innovation matters more than chemistry breakthroughs alone
-
Recycling will play a major cost role after 2030
-
Modular battery packs will reduce repair and replacement costs
These insights reflect a mature industry shifting from experimentation to optimization.
Conclusion: The Real Meaning of EV Battery Cost in 2026
The electric vehicle battery cost analysis for 2026 shows a market that is stabilizing rather than rapidly declining. While costs continue to fall gradually, the real progress lies in:
-
Longer battery life
-
Safer chemistries
-
Better recycling
-
Lower cost per mile
For consumers, manufacturers, and policymakers, battery cost is no longer just a number—it is a system-level equation involving materials, manufacturing, lifespan, and sustainability.
1 thought on “Electric Vehicle Battery Cost Analysis 2026”